Renewable Methanol: A Promising Carbon Neutral Liquid Fuel
Introduction
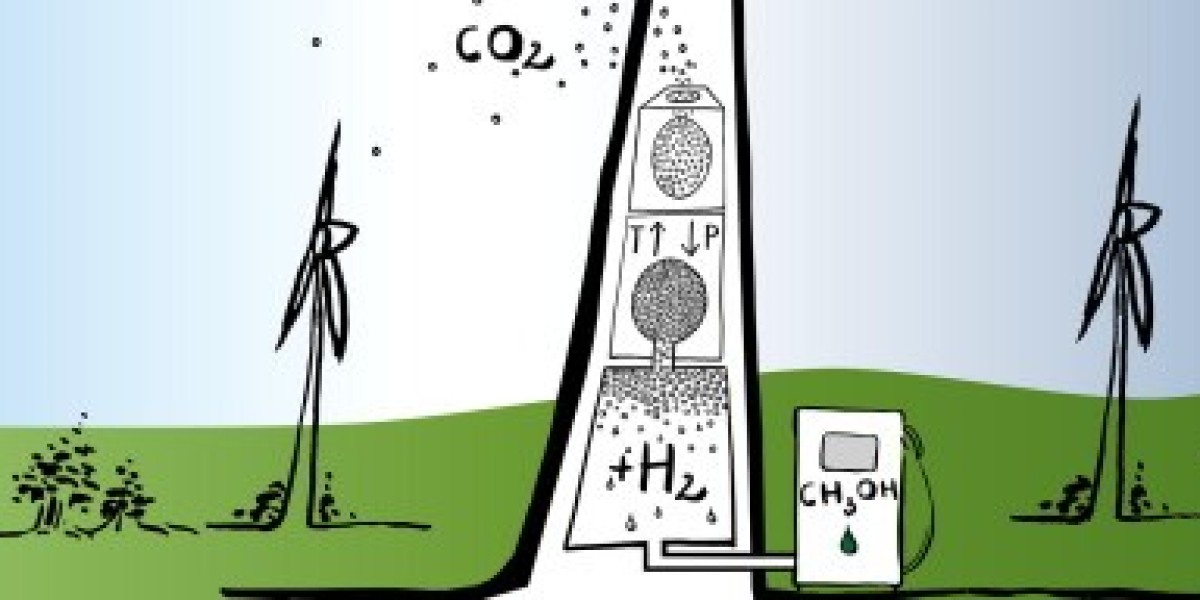
Renewable methanol is methanol that is produced from renewable resources like biomass and CO2 waste streams rather than from fossil fuels. Methanol is the simplest alcohol with the chemical formula CH3OH. It can be used as a fuel in its pure form or blended with gasoline or diesel. Traditional methanol is made through steam reforming of natural gas, but reusable methanol uses renewable feedstocks and carbon capture technologies.
The Production Process
The typical production process for reusable methanol involves four main steps:
Feedstock Collection and Processing
Biomass feedstocks like agricultural residue or waste wood are collected and processed. This may involve chipping, drying and sizing the feedstock. CO2 from industrial processes can also be captured and utilized.
Synthesis Gas Production
The feedstock is gasified in a reactor using steam, oxygen, or air to produce a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen called synthesis gas (syngas). Gasification is a high-temperature process that breaks down the chemical bonds in the feedstock.
Synthesis
Using catalysts, the syngas is converted into methanol through hydrogenation. The carbon monoxide and hydrogen react under pressure in the presence of catalysts to form methanol. Excess CO2 can also be utilized if present in the syngas.
Product Separation and Refining
The methanol product is separated, purified through distillation, and refined to the required purity level. Any byproducts are recovered and recycled or disposed of properly.
Advantages Over Fossil Fuel Based Methanol
Renewable methanol offers several environmental advantages compared to conventional methanol made from natural gas:
- Carbon neutral or negative: It does not add new carbon to the atmosphere since the carbon comes from recently absorbed biomass or waste CO2 streams. Used with carbon capture, it can be carbon negative.
- Renewable resource base: It utilizes waste biomass and industrial waste CO2 rather than finite fossil fuels. This makes it a truly sustainable fuel source.
- Lower emissions: Lifecycle analyses show reusable methanol can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 100% depending on the feedstock and technologies used.
- Resource independence: It reduces reliance on imported natural gas and petroleum. Countries can utilize their local waste resources and develop new domestic industries.
Potential Markets and Applications
There is significant potential to deploy reusable methanol across a variety of sectors to reduce carbon:
Transportation
It can be used as a marine fuel or blended with gasoline and diesel in vehicles. Methanol vehicles and infrastructure already exist worldwide, advancing the potential market. Methanol ferries and trucks are operating in Scandinavia.
Power Generation
Methanol can fuel turbines for base load power plants as well as microgrids. It offers an alternative to diesel especially in off-grid applications. Fuel cells can also use it to generate quiet, efficient electricity.
Chemical Industry
Methanol is an important chemical building block used to make many other chemicals and products. Reusable methanol as a feedstock could green this important sector.
Heating and Cooking
Methanol fuel can be used for residential and commercial heating boilers as well as cookstoves and personal fuel cells. This may improve air quality and health in developing nations.
Outlook and Barriers
The production and deployment of renewable methanol is expected to grow rapidly in the coming decades as concerns over carbon emissions escalate and technologies achieve economies of scale. However, some barriers still need to be addressed such as high capital costs, developing distribution infrastructure, and regulatory acceptance. With proper policy support, technology improvements, and market pulls, renewable methanol is poised to become a key contributor in global decarbonization efforts. Overall, it shows strong potential as a carbon neutral liquid fuel and chemical building block.