In the realm of modern construction and civil engineering, achieving stability in weak or compromised soils is paramount. Among the innovative solutions available, PP biaxial geogrid have emerged as a game-changing technology. These geosynthetic materials enhance soil strength, improve load distribution, and provide cost-effective solutions for infrastructure projects. This article delves into the mechanics, applications, benefits, and considerations of using biaxial geogrids, particularly in the Indian context.
What Are Biaxial Geogrids?
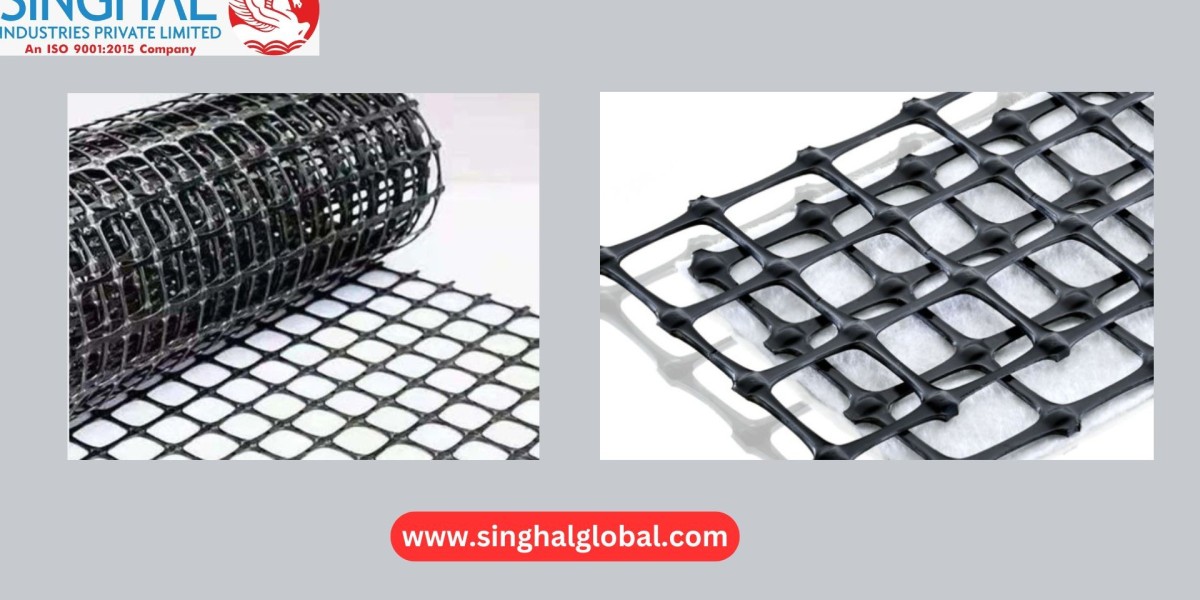
Biaxial geogrids are geosynthetic reinforcement materials designed to offer tensile strength in two perpendicular directions—longitudinal (lengthwise) and transverse (widthwise). Typically made from materials like polypropylene (PP) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), these grids are manufactured through a process of extrusion, punching, and stretching. The resulting grid structure features apertures that interlock with surrounding soil or aggregate, creating a reinforced composite system.
Mechanism of Soil Strength Enhancement
Biaxial geogrids improve soil strength by addressing two key issues: load distribution and soil displacement. When applied, these grids:
Evenly Distribute Loads: By spreading applied loads across a wider area, geogrids minimize localized stress concentrations. This reduces the likelihood of soil deformation and settlement.
Provide Tensile Reinforcement: Weak soils typically lack tensile strength. Biaxial geogrids bridge this gap by providing a reinforcing framework that prevents soil from shifting under pressure.
Enhance Friction and Confinement: The apertures in the geogrid allow for interlocking with soil or aggregate, creating a mechanically stabilized layer. This interaction increases friction and reduces the potential for lateral soil movement.
The combination of these effects results in a stronger, more durable foundation capable of supporting heavy loads, even in challenging environments.
Applications of Biaxial Geogrids
Biaxial geogrids are widely used in various construction and civil engineering applications. Some notable uses include:
Road Construction: Geogrids reinforce the subgrade and base layers in roads, enhancing durability and reducing the need for thick gravel layers.
Railway Tracks: By stabilizing ballast layers, biaxial geogrids improve track alignment and reduce maintenance requirements.
Retaining Walls: Geogrids provide lateral support, enabling the construction of steep and stable retaining walls.
Slope Protection: On embankments and slopes, geogrids mitigate erosion and enhance stability.
Foundations: They are used under foundations to improve load-bearing capacity, particularly in areas with weak or compressible soils.
Benefits of Using Biaxial Geogrids
The adoption of biaxial geogrids offers numerous advantages, making them a preferred choice in infrastructure projects:
Cost-Effective: By reducing the need for additional raw materials like gravel or sand, geogrids lower construction costs while ensuring long-term performance.
Durability: Made from high-quality materials, biaxial geogrids resist UV degradation, chemicals, and moisture, ensuring longevity in harsh environments.
Improved Efficiency: Lightweight and easy to install, these grids reduce construction time and labor costs.
Environmental Benefits: Geogrids minimize the extraction and transport of raw materials, contributing to sustainable construction practices.
Versatility: With applications ranging from roads to embankments, biaxial geogrids can be tailored to various project needs.
The Indian Market for Biaxial Geogrids
In India, the demand for Biaxial Geogrid Price has grown significantly due to rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. Polypropylene biaxial geogrids are particularly popular for their affordability and performance in diverse soil conditions.
Prices for biaxial geogrids in India range between ₹50 and ₹200 per square meter, depending on factors like material type, tensile strength, and mesh size. Bulk purchases often attract discounts, making them cost-effective for large-scale projects.
Choosing the Right Biaxial Geogrid
Selecting the appropriate biaxial geogrid depends on project-specific requirements. Key considerations include:
Tensile Strength: Match the geogrid’s strength to the load-bearing demands of the project.
Soil Type: Assess soil conditions, including cohesion, drainage, and particle size.
Application Area: Determine the grid’s purpose, whether for roads, retaining walls, or slopes.
Certifications: Choose for geogrids that meet international quality standards like ISO or ASTM.
Supplier Reputation: Choose reliable manufacturers with proven track records.
Challenges and Solutions
While biaxial geogrids offer numerous benefits, some challenges exist:
High Initial Cost: Premium geogrids may have higher upfront costs, but their long-term savings often justify the investment.
Installation Expertise: Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance. Training and expert supervision can mitigate this issue.
Limited Awareness: Increased education and awareness among stakeholders can drive adoption and ensure effective usage.
Conclusion
Biaxial geogrids represent a transformative solution for soil stabilization and infrastructure resilience. Their ability to enhance soil strength, reduce construction costs, and promote sustainability makes them indispensable in modern engineering projects. As India continues to invest in infrastructure, the adoption of innovative materials like Geogrid Suppliers in India will play a pivotal role in shaping a durable and sustainable future.
By understanding the mechanics, applications, and benefits of biaxial geogrids, engineers and builders can make informed decisions to ensure the success of their projects. With a growing market and expanding local expertise, sourcing high-quality biaxial geogrids in India has never been easier.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are biaxial geogrids made of?
Biaxial geogrids are typically made of polypropylene (PP) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE). These materials ensure durability, UV resistance, and compatibility with various soil types.
2. How do biaxial geogrids enhance soil strength?
They improve soil strength by distributing loads evenly, providing tensile reinforcement, and allowing interlocking with surrounding soil or aggregates. This creates a stabilized and durable foundation.
3. What are the primary applications of biaxial geogrids?
Biaxial geogrids are used in road construction, railway tracks, retaining walls, slope protection, and foundation stabilization. They are ideal for weak or compressible soils.