One such growing area is healthcare, where AR shows promise to enhance medical practices and patient care. Let's take a closer look at how AR is augmenting the healthcare landscape.
What is Augmented Reality?
Before delving into its uses in healthcare, it's important to understand what augmented reality is. Augmented reality enhances one's current perception of reality by overlaying digital information, images or videos onto the real world. Using devices like smartphones or AR-enabled glasses, users can access virtual information that complements their natural vision.
In healthcare, AR holds potential to provide real-time clinical information, guided surgical assistance, enhanced patient/practitioner education and more. It minimizes reliance on physical materials while making critical data readily available.
Medical Training and Education
One major use of Augmented Reality In Healthcare is for medical training and education. AR applications allow simulation of complex biological systems and medical procedures in an interactive and immersive manner.
Trainee surgeons, for example, can practice intricate procedures on virtual augmented reality patients. This improves their hand-eye coordination and procedural understanding without putting real patients at risk. Complex anatomical models can be explored from different angles using AR.
Nursing and medical students can utilize AR to learn human anatomy, visualize diseases and treatment methods. Interactive AR modules are being developed for self-paced learning on topics like pharmacology, biochemistry etc. This makes difficult concepts more engaging and easier to grasp for students.
AR is also employed to provide just-in-time information to healthcare workers. Using apps, they can identify medicines, medical equipment or access treatment guidelines while on the job. This aids decision making and eliminates errors resulting from lack of quick reference.
Remote Collaboration and Consultation
Geographical barriers pose difficulties for remote medical consultation and collaboration. AR bridges this gap by allowing real-time interactive sessions between practitioners separated by distance.
Specialized AR platforms enable face-to-face virtual meetings where doctors can discuss cases, get second opinions and demonstrate examination findings in real-time. During surgery or intervention, assisting physicians can provide guidance via AR even if not physically present.
AR telemedicine applications additionally grant remote access to patient records and parametric monitoring. Specialists can thus reliably diagnose and triage patients irrespective of location. This proves a boon for rural and underserved communities with limited local medical resources.
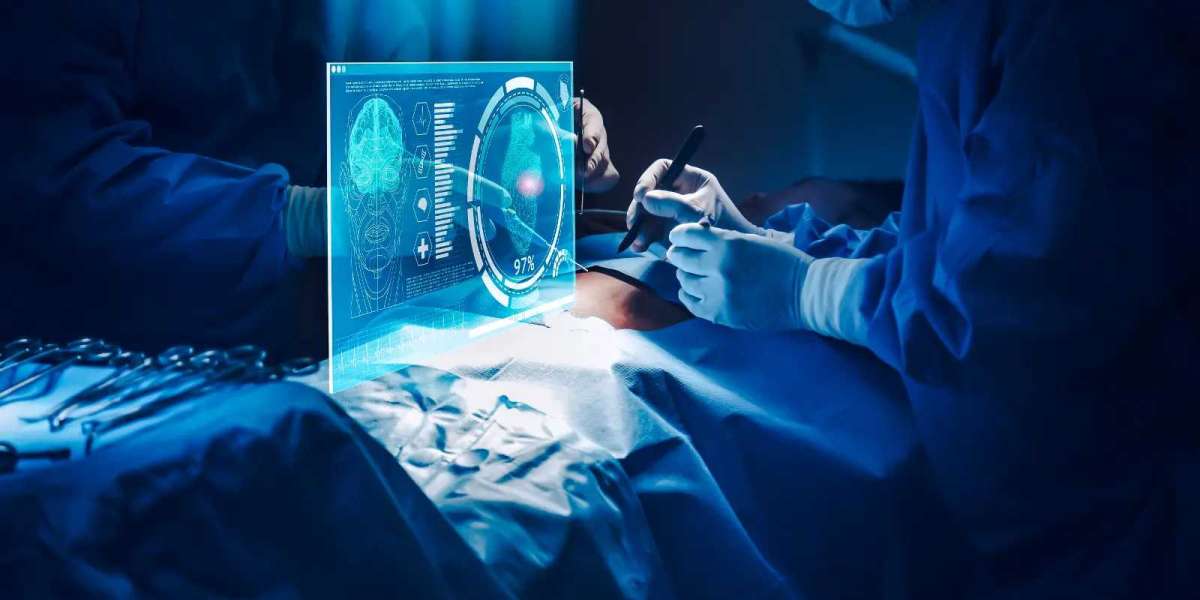
Improving Surgical Accuracy
In the operating room, AR improves surgical accuracy, precision and outcomes. Surgeons can visualize sub-surface anatomies, delicate tissues and implants overlaid on the real view of the patient.
Using AR navigation, exact resection margins or insertion points are identified, segmented tumours are removed completely and anatomical landmarks located spot-on. Complex procedures like neuro or cardiac surgeries get simpler with augmented surgical guides.
Post-surgical AR also aids evaluation of treatment effectiveness and detection of residual/recurrent pathologies. Integrated MRI, CT and previous scans provide before-and-after comparisons to optimize follow-up planning.
In vascular or ophthalmic surgeries, AR helps track device positioning, vessel access and tissue manipulation in real-time instead of relying on X-rays alone. Risks of radiation exposure are therefore reduced.
Get More Insights On This Topic: Augmented Reality in Healthcare