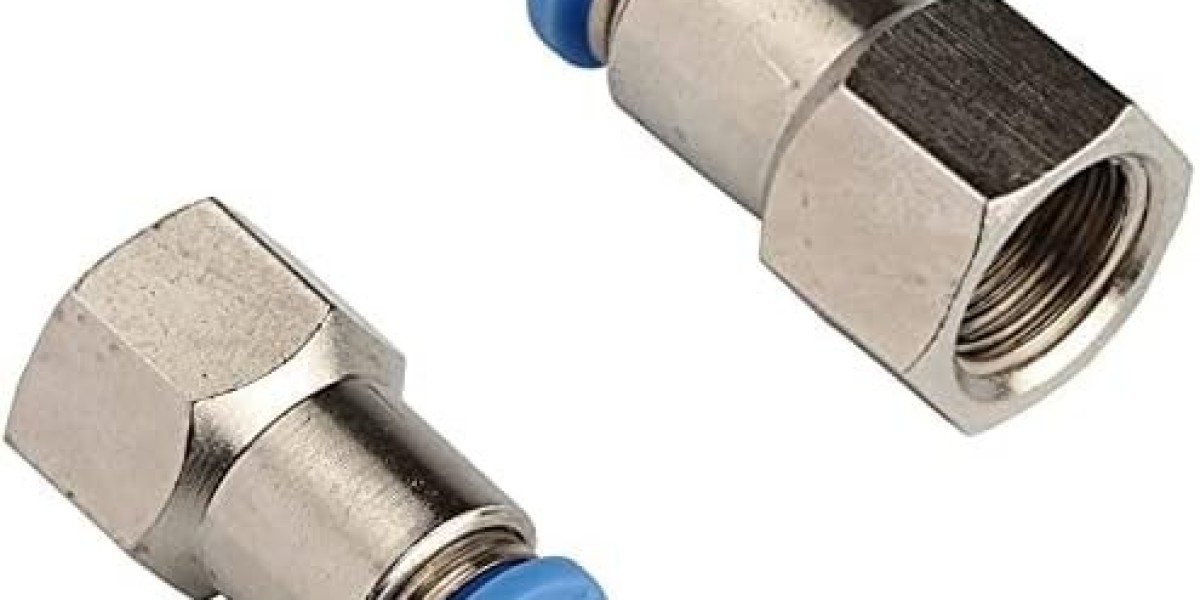
Female fittings are crucial components used in piping systems to connect pipes or tubes. These fittings have internal threads that allow them to join with male fittings, which have external threads. This connection forms a secure, leak-proof seal, ensuring that fluid or gas flows smoothly through the system. Female fittings are found in many applications, from residential plumbing to industrial systems, and they play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the piping system.
What Are Female Fittings?
Female fittings are pipe connectors designed with internal threads that enable them to connect to male fittings. These fittings are often used to join two pipes or tubes of different sizes or materials. Female fittings are available in various shapes and sizes, such as elbows, tees, couplings, and reducers, to meet the specific needs of the piping system.
How Do Female Fittings Work?
Female fittings work by connecting to male fittings, which have external threads that screw into the internal threads of the female fitting. When the male fitting is screwed into the female fitting, a tight seal is formed, preventing leaks and ensuring that the pipes stay securely connected. This process allows fluid, gas, or air to flow seamlessly through the pipes without interruptions.
Key Functions of Female Fittings in Piping Systems
Connecting Pipes: The main function of female fittings is to connect pipes or tubes in various systems, such as water supply, gas lines, and industrial applications. The internal threads of the female fitting allow it to create a tight seal with male connectors.
Maintaining System Integrity: Female fittings help maintain the integrity of the piping system by ensuring that the connections are secure and leak-free. This is especially important in systems that carry hazardous or pressurized fluids and gases.
Enabling Flexibility in Design: Female fittings allow for flexibility in designing piping systems. They can be used in combination with other fittings, such as elbows and tees, to create complex pipe layouts for different applications.
Easy Installation and Maintenance: Female fittings are easy to install and maintain. The threaded connection makes them simple to assemble and disassemble without the need for welding or other complicated methods. This helps save time and effort during installation and repairs.
Types of Female Fittings
Female fittings come in various types, each designed for specific purposes. Some of the most common types include:
- Elbow Female Fittings: Used to change the direction of flow in a piping system by connecting two pipes at an angle.
- Tee Female Fittings: Used to connect three pipes together, forming a "T" shape to divert the flow in different directions.
- Coupling Female Fittings: Used to join two pipes of the same size, creating a continuous pipe line.
- Reducer Female Fittings: Used to connect pipes of different sizes, allowing the flow of fluid from a larger pipe to a smaller one.
Applications of Female Fittings
Female fittings are used in various industries, including:
- Plumbing: In residential and commercial plumbing, female fittings connect water supply lines, drains, and fixtures.
- Oil and Gas: Female fittings are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines to connect tubes that carry petroleum and natural gas.
- Automotive: In automotive systems, female fittings are used in fuel, coolant, and brake lines to ensure secure and leak-free connections.
- Industrial Systems: Female fittings are also used in industrial piping systems to carry steam, chemicals, and other fluids.
Conclusion
Female fittings are essential components in piping systems, providing secure and reliable connections between pipes. Their ability to form tight, leak-proof seals with male fittings makes them crucial for maintaining the integrity of the system. Whether in plumbing, oil and gas, or industrial applications, female fittings ensure that fluids and gases flow smoothly and safely through pipes. By choosing the right type of female fitting for the application, you can help ensure the efficiency and longevity of the piping system