What We Do
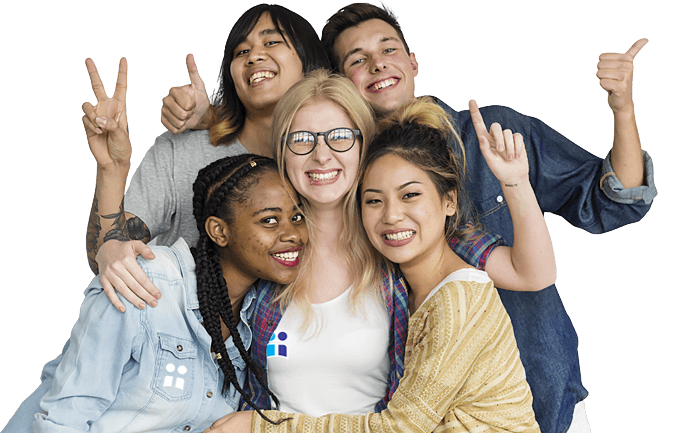
Why Join Our Biiut from Social Network ?
When you meet anyone, treat the event as a holy encounter. It's through others that we either find or love our self. For you see, nothing is accomplished without others. When you eliminate the concept of separation from your thoughts and your behavior, you begin to feel your connection to everything and everyone..
Join Our Community-
Meet Great People
People value is not measured by the number of people we meet but by the number of people we introduce to others.
-
Discussion
Discussion is an exchange of knowledge; an argument an exchange of ignorance..
-
Active Groups
Ideas grow better when transplanted into another mind than the one where they sprang up..