Performance Fabric Allows Athletes to Achieve Peak Performance
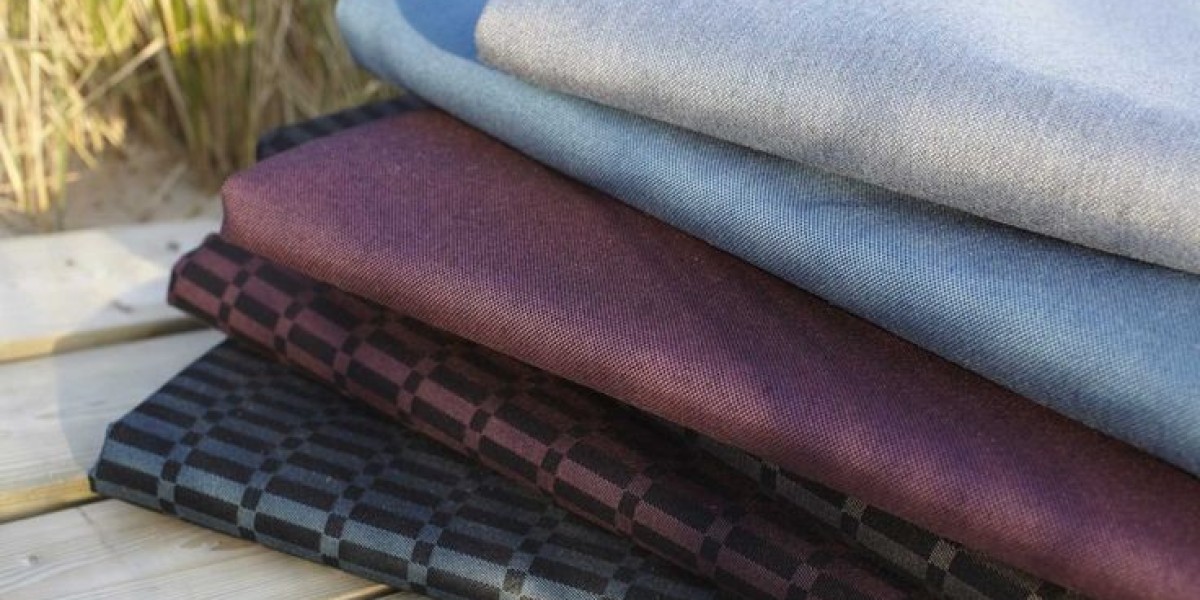
Performance fabrics have revolutionized the sports apparel industry by using advanced materials and technologies to help athletes achieve peak performance. These technical fabrics are engineered to keep athletes cool, dry and comfortable during even the most intense workouts and competitions. Some of the key properties and functions of performance fabrics include:
Moisture-Wicking Ability
One of the most important functions of a Performance Fabric is its ability to wick moisture away from the skin. Fabric that can quickly pull sweat away from the body and move it to the outer layers helps prevent athletes from feeling wet or soggy. This keeps them dry and promotes evaporation, helping them maintain a comfortable body temperature even when working out in hot or humid conditions. Many performance fabrics use engineered fibers that act like tiny sponges to absorb liquid before rapidly transporting it to the fabric surface for evaporation.
Breathability
To optimize comfort during activity, a performance fabric must be breathable to allow sweat and moisture to escape from the garment. Highly breathable fabrics prevent athletes from overheating by permitting air circulation next to the skin. Advanced moisture management and breathable fabrics work together to provide a continuously dry microclimate against the body. This keeps skin temperatures regulated for enhanced endurance and comfort.
Fit and Range of Motion
An ideal performance fabric allows complete freedom of movement without impairing athletic performance. Engineers design fabrics with four-way stretch and other technologies to form-fit the body securely without restriction. The stretchy, form-fitting material enables a full range of motion for any type of athletic activity, from running to gymnastics. Some fabrics even incorporate compression qualities for added muscle support.
Antimicrobial Protection
Since sweat and heat are generated during exercise, performance fabrics employ antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. These prevent the growth of odor-causing microbes that can develop due to moisture. Eliminating bacteria and fungus minimizes odors so clothes stay fresh longer between washes. Antimicrobial fibers also offer an added layer of protection against infections for active lifestyles.
Environmentally Friendly Production
As consumer demand for sustainable apparel increases, manufacturers are turning to eco-friendly processes and renewable resources. Many top performance fabric brands focus on minimizing their environmental impact and using greener technologies. Some examples include utilizing recycled polyester fiber from plastic bottles, employing organic cottons, and utilizing zero-discharge dyeing methods that produce no wastewater. This helps materials maintain their moisture-wicking and other technical qualities while being produced responsibly.
Innovative New Performance Fabrics
Fiber and textile engineers constantly evolve performance fabrics to push the boundaries of comfort, fit and function. Here are some cutting-edge materials leading the way:
Phase Change Materials
Incorporating phase change materials (PCMs) allows fabrics to actively regulate body temperature. PCMs absorb, store and release heat via a chemical reaction rather than just passively wicking moisture. This helps fabrics feel cooler when the body warms and vice versa for enhanced thermoregulation. Some shirts contain PCMs microencapsulated within the fibers.
Natural Performance Materials
While most performance fabrics traditionally used synthetic fibers, renewable natural materials are gaining popularity. Examples include bamboo, tropical wool and tencel made from wood pulp. These feel soft and breathable while providing moisture control, stretch, and other technical properties on par with synthetics. They offer the benefits of natural materials with high-performance functionality.
Nano Fibers and Textiles
Nanofibers and nanotextiles engineered at the microscopic level unlock new possibilities. For example, nano-silver fibers embedded in fabric can self-clean via a photocatalytic reaction and provide built-in antimicrobial qualities. Nano cross-linking during fabric production results in ultra-soft handfeel, moisture transportation and other enhanced properties. The future potential of these innovations remains largely untapped.
The Global Rise of Performance Fabric
As fitness and activewear gain mainstream popularity worldwide, performance fabrics have become integral threads in the global sports apparel industry. Research firm Grand View Research reports the global performance fabric market size was valued at $23.42 billion in 2019 and predicts it will grow at a 6% compound annual rate through 2027. Some key industry statistics:
- North America currently dominates at 32.6% of global market share, but Asia Pacific is projected to become the fastest growing regional market.
- Activewear, outdoor and athletic-inspired fashion are major drivers as exercise participation increases globally and lines blur between performance and everyday casual wear.
- Leading brands continuously innovate new performance fabrics while partnering with top athletes to showcase how these materials enable pushing limits.
- Polyester dominates at 35.4% of production volumes due to favorable properties like stretch, durability and moisture transport. However, natural and sustainable alternatives are gaining traction.
As science harnesses new materials at the nanoscale and cellulose-based fabrics evolve, the future possibilities for performance apparel appear limitless. Advanced moisture management, thermoregulation, elasticity, antibacterial qualities and other high-tech textiles set to conquer new frontiers will surely drive ongoing industry growth in the decade ahead.
Get More Insights on- Performance Fabric
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want:
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)