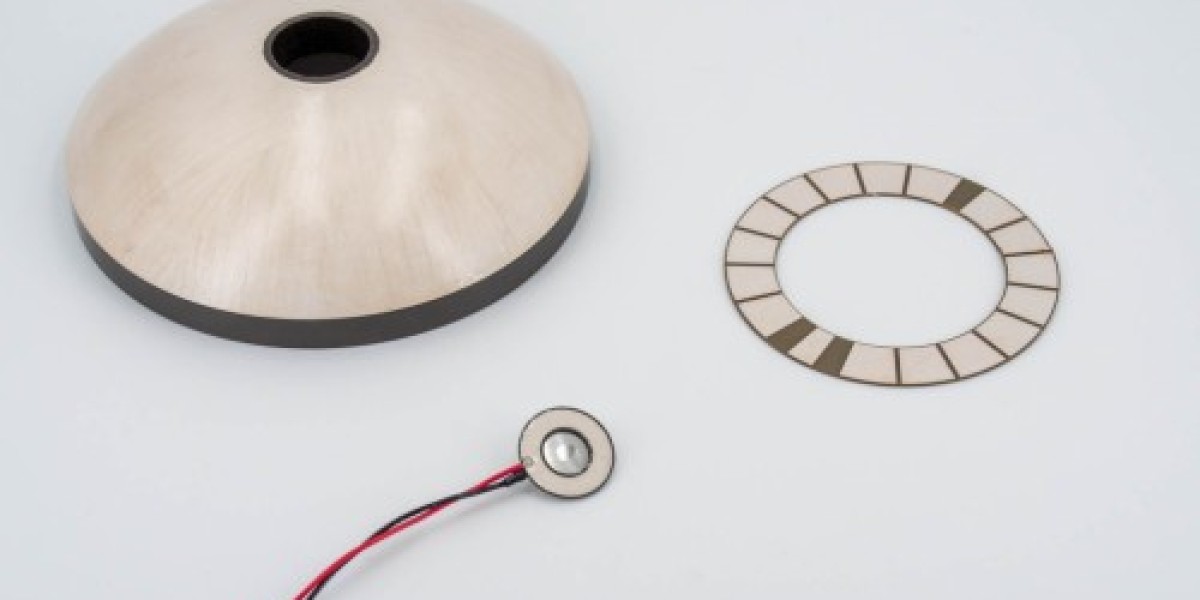
Ultrasonic piezoelectric transducers are widely used in industrial, medical, and scientific applications for precision sensing, non-destructive testing, and imaging. These transducers rely on the piezoelectric effect to generate and receive ultrasonic waves, allowing them to detect objects, measure distances, or transmit signals.
However, like any electronic component, ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer can encounter issues that impact performance. Whether it’s signal degradation, reduced sensitivity, or complete failure, understanding how to troubleshoot these problems can save time, reduce downtime, and improve efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll explore common problems with ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer, their possible causes, and effective troubleshooting methods to keep them running optimally.
- Weak or No Ultrasonic Signal Output
Possible Causes:
- Electrical connection issues (loose or damaged wires)
- Faulty power supply or voltage fluctuations
- Degraded piezoelectric material
- Incorrect frequency selection
- Damaged transducer surface or diaphragm
Troubleshooting Steps:
✔Check power supply: Ensure the transducer is receiving the correct voltage and power level required for operation. Low voltage can reduce signal output.
✔Inspect wiring: Look for any loose or broken connections in the transducer circuit. Secure or replace damaged wiring.
✔Test the transducer with an oscilloscope: This helps verify if the transducer is generating an ultrasonic signal at the correct frequency.
✔Clean the transducer surface: Dirt, debris, or damage on the radiating surface can weaken signal transmission. Use gentle cleaning methods and avoid abrasive materials.
✔Verify frequency compatibility: Using an incorrect frequency transducer for the system can lead to weak signals. Ensure that the transducer matches the device’s required frequency.
- Reduced Sensitivity or Poor Detection Performance
Possible Causes:
- Aging or worn-out piezoelectric material
- Interference from surrounding devices
- Incorrect alignment of the transducer
- Temperature fluctuations affecting performance
Troubleshooting Steps:
✔Test with a reference object: If the transducer is used for distance measurement or object detection, verify performance with a standard object at a known distance.
✔Eliminate interference: Keep the transducer away from other electronic devices that may produce electromagnetic noise.
✔Check for temperature effects: Some piezoelectric materials lose efficiency at extreme temperatures. If possible, operate the transducer in a stable environment.
✔Replace aging transducers: If the sensitivity is continuously dropping despite troubleshooting, the piezoelectric element may have degraded and need replacement.
- Erratic or Unstable Readings
Possible Causes:
- Inconsistent power supply
- Mechanical vibrations affecting stability
- Software or signal processing issues
- Environmental factors like humidity or dust accumulation
Troubleshooting Steps:
✔Stabilize the power supply: Use a regulated power source to avoid fluctuations in input voltage.
✔Secure the transducer mount: Ensure the transducer is properly mounted to avoid mechanical vibrations that can create erratic readings.
✔Filter noise in the signal: Implement signal filtering techniques in the software to remove unwanted noise from readings.
✔Keep the transducer clean: Humidity and dust accumulation on the sensor face can impact readings. Regularly clean and inspect the transducer for any physical obstructions.
- Overheating of the Transducer
Possible Causes:
- Continuous high-power operation
- Poor heat dissipation
- Overvoltage or electrical issues
Troubleshooting Steps:
✔Reduce power load: If possible, operate the transducer at a lower power setting or use pulsed operation instead of continuous mode.
✔Improve cooling and ventilation: If the transducer is enclosed, ensure proper airflow to dissipate heat. Adding heat sinks or cooling fans may help.
✔Check voltage levels: Overvoltage can cause excessive heating. Ensure the transducer operates within its recommended voltage range.
✔Monitor duty cycles: Avoid running the transducer for extended periods without breaks, especially in high-power applications like industrial cleaning or sonography.
- Complete Transducer Failure
Possible Causes:
- Electrical burnout due to overvoltage
- Mechanical damage from physical impact
- Manufacturing defects
- Aging and wear over time
Troubleshooting Steps:
✔Perform a continuity test: Use a multimeter to check for open circuits in the transducer wiring. A broken circuit means the transducer needs replacement.
✔Look for visible damage: If the ceramic element or housing is cracked, the transducer is likely beyond repair.
✔Replace damaged components: If the transducer has detachable parts, replacing a faulty element may restore functionality.
✔Consult the manufacturer: If the transducer is still under warranty, contact the manufacturer for a replacement or repair service.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
To extend the lifespan of an ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer, follow these best practices:
Regular cleaning: Remove dust, debris, and contaminants from the transducer surface.
Proper storage: Store transducers in a dry, temperature-controlled environment when not in use.
Avoid excessive voltage: Stay within the recommended power specifications to prevent burnout.
Periodic calibration: Calibrate transducers regularly to maintain accuracy in measurements.
Check connections: Inspect and secure electrical connections periodically to prevent performance drops.
Conclusion
Understanding and troubleshooting common issues in ultrasonic piezoelectric transducers can prevent downtime, improve accuracy, and extend the device’s lifespan. Whether you’re experiencing weak signals, unstable readings, overheating, or complete failure, following these troubleshooting steps can help diagnose and fix problems efficiently.
By maintaining your ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer properly and taking preventive measures, you can ensure optimal performance and reliability in industrial, medical, and scientific applications.