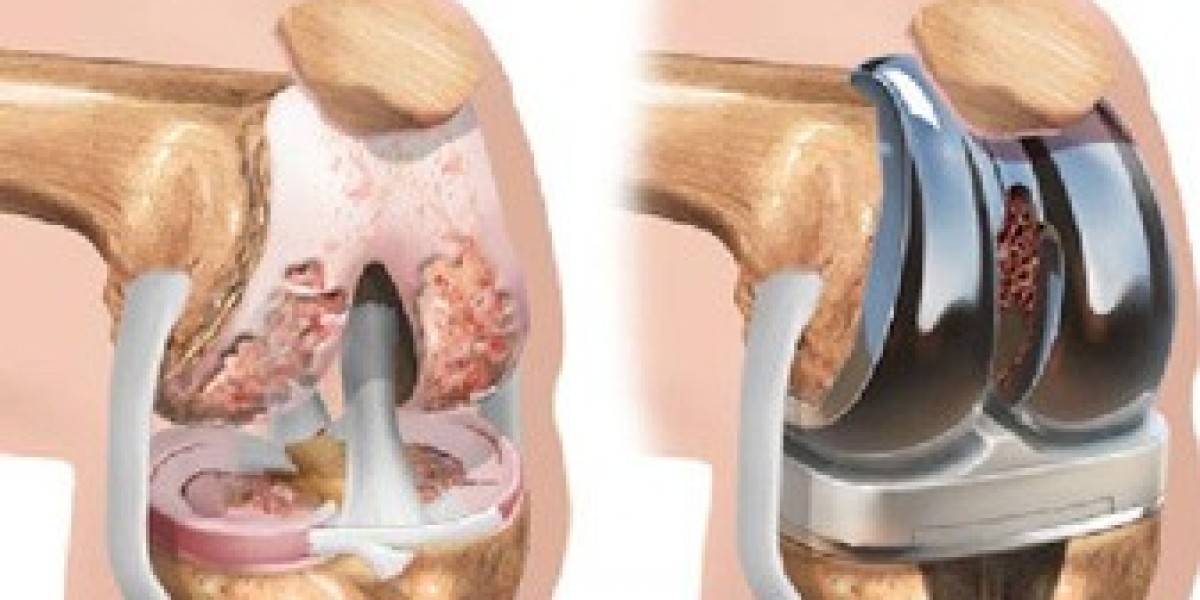
Knee replacement surgery requires thorough pre-surgery evaluation, pain management, and lifestyle adjustments. Post-surgery, patients undergo physical therapy, manage pain, and follow recovery guidelines. Successful outcomes depend on preparation, rehabilitation, and realistic expectations for long-term results.
Before Knee Replacement Surgery
Pre-Surgery Evaluation:
- Physical Exam and Imaging: Doctors perform a physical examination and imaging tests (X-rays, MRIs) to assess the extent of knee damage and determine if surgery is necessary.
- Blood Tests: Blood work is conducted to assess general health, including kidney function, blood clotting ability, and other health markers.
Pain Management and Non-Surgical Options:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain relievers are often prescribed to manage pain.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation or provide temporary pain relief.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and delay the need for surgery.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Weight Loss: Being overweight increases stress on the knee joint. Losing weight can reduce pain and help improve the outcome of surgery.
- Assistive Devices: If needed, patients may use crutches, a knee brace, or a walker to improve mobility and reduce pain during daily activities.
Surgical Decision:
- Assessment of Joint Damage: Surgery is typically recommended if conservative treatments (like medication and physical therapy) fail, and the patient’s quality of life is significantly impacted by chronic knee pain and immobility.
- Final Decision: The patient and surgeon will discuss the benefits, risks, and the expected outcome. They’ll decide if knee replacement is the best treatment option.
Pre-Surgery Instructions:
- Medications: Patients are instructed to stop taking certain medications (like blood thinners) a few days before surgery to reduce bleeding risks.
- Fasting: Patients are usually asked to fast for 8-12 hours before surgery, as anesthesia can be risky if the stomach is full.
- Home Preparation: Patients should prepare their home for recovery by setting up a comfortable resting area and arranging for help with daily activities, as mobility will be limited initially.
Psychological and Emotional Readiness:
- Mental Preparation: Surgery can be emotionally daunting, so understanding the procedure, setting realistic expectations, and preparing for the recovery process is essential.
- Support System: A strong support system of family and friends is beneficial to ease the emotional strain during the recovery process.
After Knee Replacement Surgery
Post-Surgery Hospital Stay:
- Recovery Room: After surgery, patients are monitored in the recovery room until the anesthesia wears off. This may last several hours.
- Hospital Stay: Most patients stay in the hospital for 1-3 days, depending on their condition and how well they’re recovering.
Pain Management:
- Initial Pain: Post-surgery pain is expected, and pain management is a critical part of the recovery process. Doctors may administer pain relievers and local anesthesia to control discomfort.
- Medications: Pain medications (such as opioids, NSAIDs, or nerve blockers) will be prescribed to manage pain in the days following surgery.
- Ice and Elevation: Applying ice and elevating the leg can help reduce swelling and manage pain.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
- Early Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation begins within 24-48 hours of surgery. The goal is to restore range of motion, prevent complications, and ensure that the knee heals properly. Simple exercises, like bending and straightening the knee, will be done in the early days.
- Strengthening: As recovery progresses, exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and other leg muscles will be introduced.
- Long-Term Therapy: Physical therapy continues for 3-6 months after surgery, and exercises will become more challenging to help regain strength and flexibility.
Post-Surgery Limitations:
- Limited Movement Initially: Patients may have limited movement for the first few weeks and are encouraged to take short walks to prevent blood clots.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: Running, jumping, or activities that put excessive strain on the knee joint should be avoided to ensure the longevity of the implant.
- Mobility Aids: Patients will likely use crutches, walkers, or canes initially to help with mobility as the knee heals.
Managing Swelling and Bruising:
- Swelling: Swelling is common post-surgery and can last for several weeks to months. Ice packs and elevation help alleviate this.
- Bruising: Some patients may experience bruising around the knee joint, which usually fades within 2-4 weeks.
Regaining Mobility:
- Early Recovery: Most patients can walk with assistance (crutches or a walker) within a few days to weeks after surgery.
- Gradual Improvement: Over time, walking becomes easier, and patients can resume light daily activities like cooking, dressing, or going up and down stairs.
- Driving: Driving is typically not recommended for 4-6 weeks, or until patients regain enough strength and mobility in the knee to safely operate a vehicle.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Low-Impact Activities: Once fully recovered, patients are encouraged to engage in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling to keep the knee functioning well without overstraining it.
- Avoiding High-Impact Sports: High-impact sports (e.g., running, tennis) should be avoided to preserve the longevity of the knee implant.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the knee joint and extends the life of the artificial knee.
Complications and Risks:
- Infection: Although rare, infections can occur at the surgical site. Infections may require further treatment or surgery.
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) is a risk in the early days of recovery, so preventive measures like blood thinners and mobility exercises are critical.
- Implant Failure: The knee implant may eventually wear out or loosen, requiring revision surgery. This is more likely in younger, more active individuals.
Psychological Adjustments:
- Emotional Recovery: Recovery can be emotionally challenging as patients adjust to their new knee. Support from family, friends, and physical therapists is crucial to navigating this process.
- Realistic Expectations: Some patients may feel frustrated during recovery, especially if progress is slower than expected. Staying realistic and patient during this phase is key to long-term success.
Long-Term Results:
- Improved Quality of Life: For most patients, knee replacement significantly improves pain levels, mobility, and overall quality of life. Many report being able to return to normal activities and enjoy a more active lifestyle.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regular check-ups with the surgeon and continued attention to physical activity and weight management are essential to ensure long-term success.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery is a life-changing procedure that offers significant benefits for those suffering from severe knee pain. However, the journey before and after surgery requires careful preparation, commitment to rehabilitation, and realistic expectations. Following the appropriate steps before surgery, including managing pain and preparing for recovery, and engaging in the right physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments after surgery, ensures the best possible outcomes for patients.